Rotablation
Rotablation
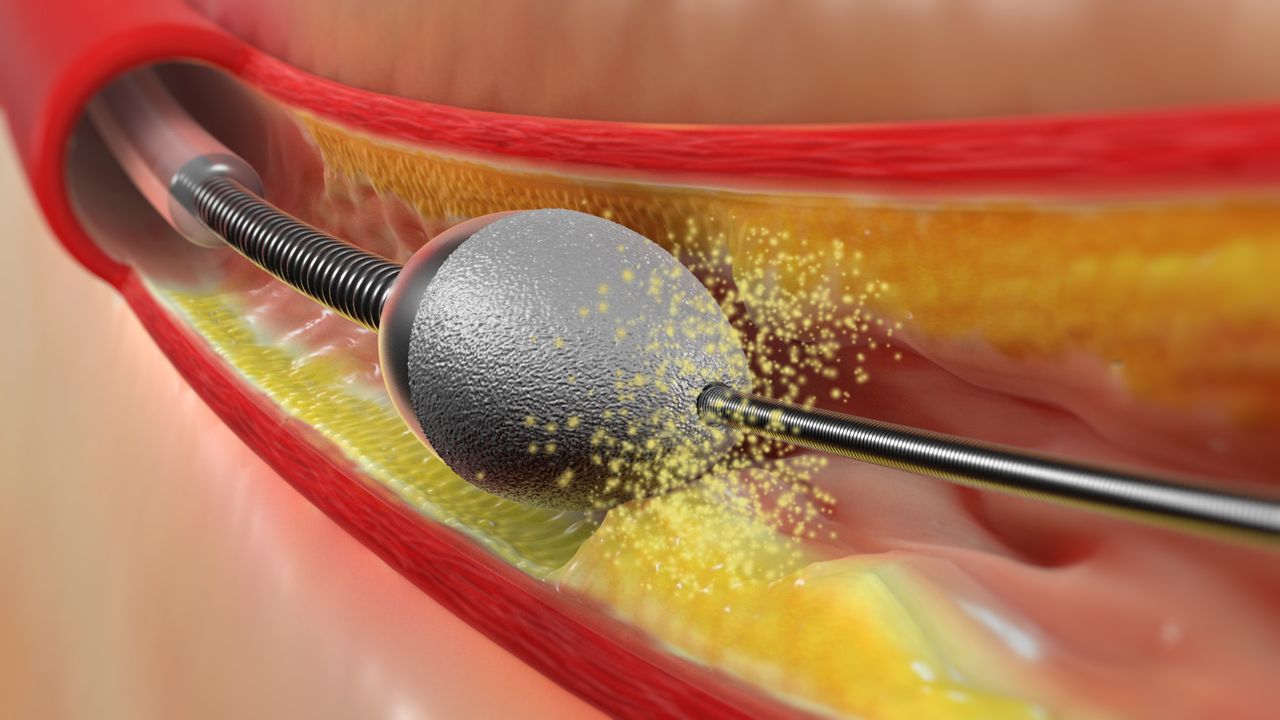
Rotablation uses a tiny drill with a diamond-tipped burr, powered by compressed air to break up calcified plaque (hard block) that is clogging the coronary artery. Breaking up the plaque restores blood flow to the heart.
The procedure of coronary angioplasty is performed in the cardiac catheterization laboratory (or cath lab) by a specialized Interventional cardiologist. Angiogram is performed prior to an angioplasty. From the digital pictures thus obtained of the contrast material, one can find out whether the coronary arteries are narrowed. The two types of angioplasty techniques are balloon angioplasty and stenting. Dr. Sengottuvelu pioneered the radial angiogram procedures in India leading to day care procedures with same day discharge.
Rotablation
Rotablation represents an addition to the standard PCI procedure. While a standard PTCA procedure is limited to the use of balloons and stents, rotablation also uses a tiny drill, powered by compressed air, to remove calcified deposits. Breaking up the plaque restores blood flow to the heart. A catheter is introduced and advanced to the coronary artery. The guide wire is used to cross the stenosis inside the coronary artery. The drill head is used to remove plaque deposits. The burr (drill) is introduced into the artery through a catheter (tube) and after activation is passed through the narrowed portion up and down repeatedly until the block is scrapped and artery widened. Following this regular PCI is performed with stent and balloon.
Rotablation is indicated when the plaque build up inside the arteries are hard with calcific deposits. When there are large calcium deposits, the blocks are hard and conventional balloon angioplasty may not work to widen the artery. Hence patients who have moderate to severe calcium causing the block, rotablation helps to drill and grind the blocks followed by balloon and stent.
Book Appointment


Our cardiologist provides top-notch care tailored to your individual needs. From prevention to treatment, we ensure your heart is in the best hands.
About Doctor
For Appointment
Contact us
